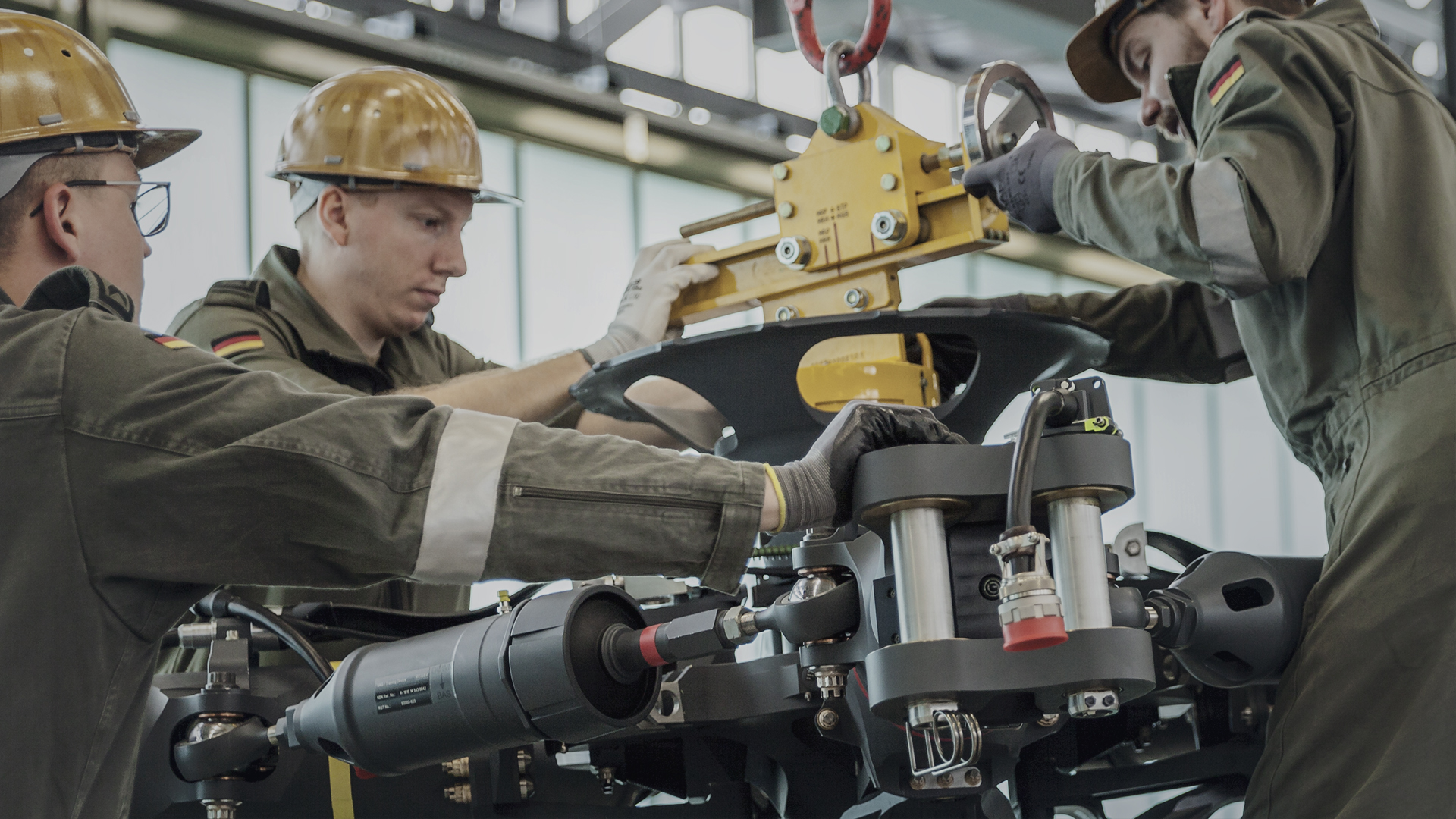
Maintenance Training Rig
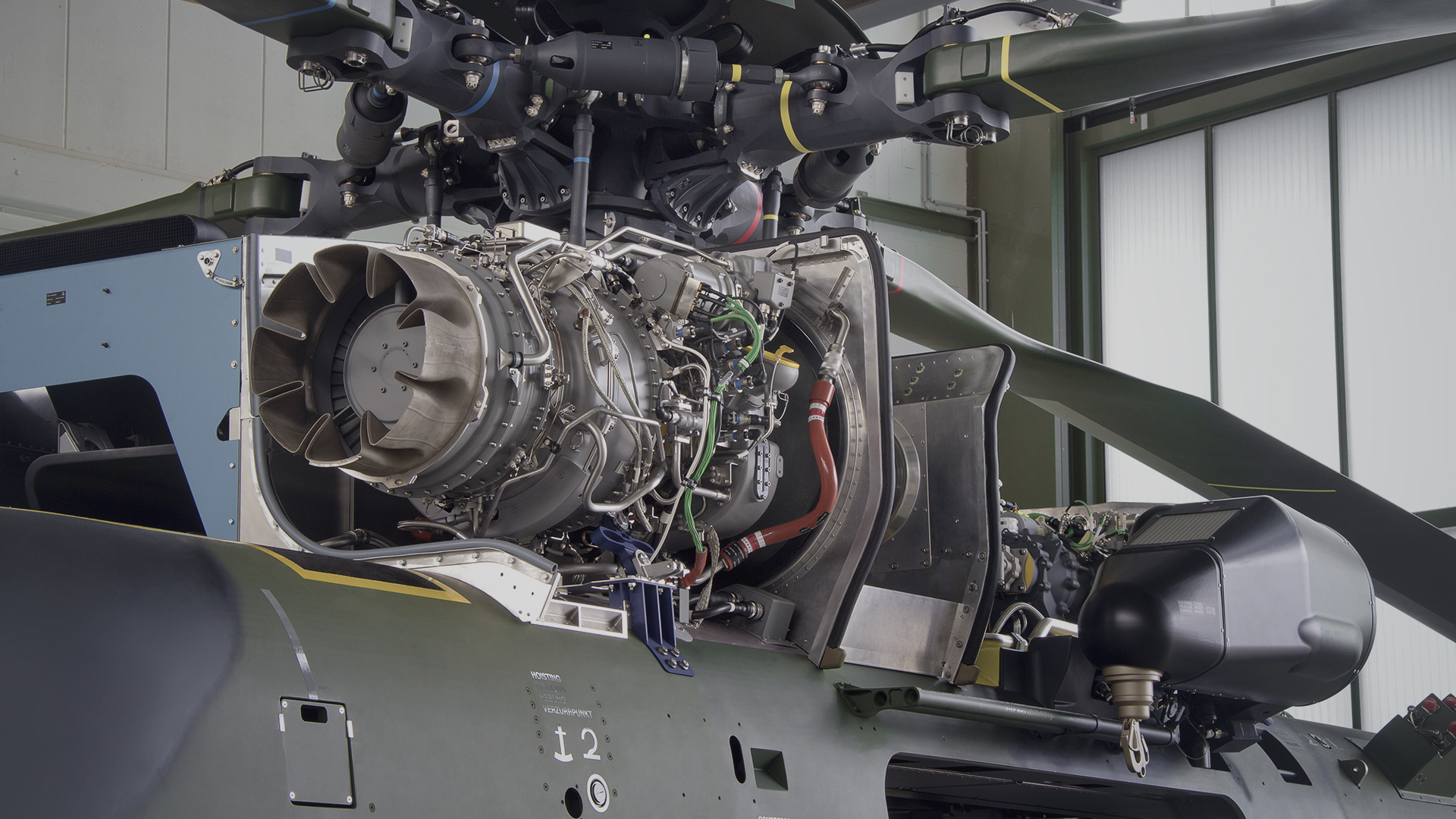
Modern and complex aircraft like the NATO NH90 Helicopter reduce pilot workload by employing high-tech solutions. A flight control computer interprets pilot commands and ensures that the aircraft performs the commanded maneuvers. Elaborate computers monitor the aircraft systems in flight and only highlight to the flight crew when an exceedance of threshold parameters is registered. This level of complexity imposes new challenges on the training of the ground crews.
It has been common practice that whenever an operator fields a fleet of aircraft, one or more of these aircraft goes to ground crew training. So the operational fleet always comes up with one or more aircraft short. Additionally, flight equipment design focuses on lightweight and is constructed for a limited number of flight hours and exchange cycles. This usually results in considerable demand for spares and repairs on the training side. Being original aircraft equipment, both training and the operational side are competing for the limited spare resources. It is not hard to imagine who gets the available spares.
Using replicated items for the crews implies 24/7-access to hands-on training without having to tie up a real helicopter. This ensures the highest training quality without reducing the flying fleet. The MTR design does not necessarily rely on OEM data. The successful concept is based on an in-house data gathering process performed on original aircraft using a wide range of technologies, from manual data gathering to high-resolution 3D scanning. This unique approach can be applied on any platform, be it a military transport aircraft like the A400M or a modern start-of-lifecycle airliner aircraft.
Precision and Durability for Uninterrupted Training
Maintenance Training Rigs (MTR) and Part Task Trainer (PTT) are designed for line maintenance training skill level based on DEMAR 66 CAT A, CAT B1 and CAT B2.
The following skills can be trained exemplary:
- EOriginal Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) maintenance instructions usage
- EMechanical system familiarization and handling
- EElectrical system familiarization and handling
- EAvionic system familiarization and handling
- EWeapon and safety system familiarization and handling
- ECheck of proper aircraft system function via e.g. control tests and built-in tests
- ETraining of fault isolation and correction

